Guar Gum Applications in Pharmaceutical Formulations
In the complex and highly regulated world of pharmaceutical formulations, excipients play a vital role in ensuring the efficacy and stability of drug products. Among the various natural polymers used, guar gum stands out as a highly biocompatible excipient.
As a leading guar gum supplier, Sunita Hydrocolloids understands the intricate demands of the pharmaceutical industry and the pivotal contributions of high-quality guar gum to innovative drug delivery systems.
Why Choose Guar Gum for Your Pharmaceutical Formulations?
Guar gum is composed primarily of a galactomannan, its unique molecular structure allows it to hydrate rapidly in water, forming highly viscous solutions or gels even at low concentrations. This property, coupled with its non-toxic, non-allergenic, and biodegradable nature, makes it an attractive excipient in various pharmaceutical applications.
The global pharmaceutical excipients market was valued at approximately USD 8.37 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, with natural excipients like guar gum playing an increasingly important role due to their favorable safety profiles.
Beyond its pharmaceutical relevance, guar gum’s unique physicochemical properties—such as high viscosity, water solubility, and biodegradability—make it a valuable ingredient across multiple sectors. From oil drilling to textiles and cosmetics, its versatility is well-documented. You can explore more about the industrial applications of guar gum to understand how this natural polymer supports innovation across industries.
Key Applications of Guar Gum in Pharmaceutical Formulations
The multifaceted properties of guar gum lend themselves to a wide array of applications in both solid and liquid pharmaceutical dosage forms:
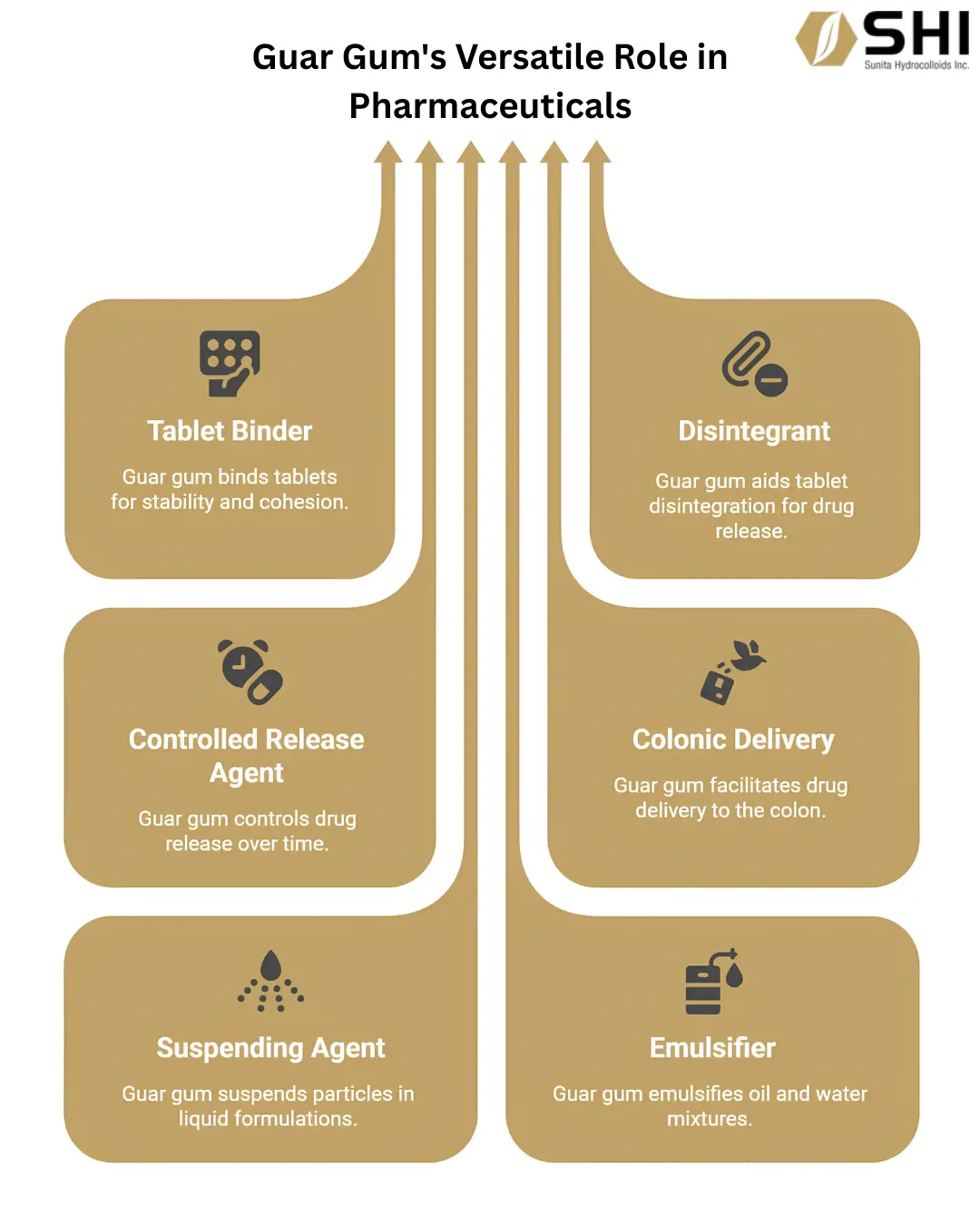
1. Tablet Binding and Disintegration
A. Binder
In tablet manufacturing, guar gum acts as an effective dry binder. Its excellent compressibility and flow properties contribute to the formation of compact, robust tablets with sufficient mechanical strength to withstand handling and packaging. This reduces friability (tablet crumbling) and ensures consistent dosage.
Research published in the International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Applications frequently highlights the efficacy of natural binders, such as guar gum, in comparison to synthetic alternatives because they are safer and more economical.
B. Disintegrant
Paradoxically, guar gum can also function as a disintegrant in tablets, particularly in higher concentrations or when used in combination with other disintegrants. Its ability to swell rapidly upon contact with water causes the tablet to break apart into smaller particles, facilitating faster drug dissolution and absorption. This dual functionality offers formulators flexibility in achieving desired drug release profiles.
2. Controlled and Sustained Drug Release Systems
This is arguably one of the most significant applications of guar gum in modern pharmaceuticals. Its gelling properties enable the development of advanced drug delivery systems designed to release the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) over an extended period, improving patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes.
A. Matrix Formulations
Guar gum can form a hydrophilic matrix within tablets or capsules. When the dosage form comes into contact with gastrointestinal fluids, the guar gum hydrates and swells, forming a viscous gel layer that controls the diffusion of the drug from the matrix. The rate of drug release can be modulated by varying the concentration of guar gum and other excipients. This is particularly valuable for drugs with short half-lives or those requiring consistent blood levels.
B. Colonic Drug Delivery
Given its resistance to enzymatic degradation in the upper gastrointestinal tract, guar gum is extensively explored for targeted drug delivery to the colon. The colonic bacteria possess enzymes (e.g., galactomannases) capable of degrading guar gum, leading to a localized release of the drug in the colon. This approach is beneficial for treating local inflammatory bowel diseases (e.g., Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis) or for systemic absorption of drugs that are optimally absorbed in the colon.
Studies published in journals like Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy have showcased the potential of guar gum in delivering drugs like 5-aminosalicylic acid directly to the colon.
3. Suspending and Emulsifying Agent
A. Suspensions
In liquid oral formulations, guar gum serves as an excellent suspending agent. It increases the viscosity of the vehicle, preventing the rapid sedimentation of insoluble drug particles and ensuring dose uniformity throughout the product’s shelf life. This is critical for patient safety and accurate dosing, especially for pediatric and geriatric populations.
B. Emulsions
Guar gum also acts as a stabilizer in pharmaceutical emulsions (e.g., lotions, creams, or oral emulsions). It helps prevent the separation of immiscible liquid phases, contributing to the stability and aesthetic appeal of the final product.
4. Ophthalmic Formulations
The lubricating and moisturizing properties of guar gum make it suitable for use in ophthalmic solutions and artificial tear formulations. It can enhance the residence time of the drug on the ocular surface and provide soothing relief for dry eye conditions.
5. Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements
Beyond pharmaceuticals, guar gum finds extensive use in nutraceuticals and dietary supplements, primarily as a source of soluble dietary fiber. It is incorporated into formulations aimed at digestive health, weight management, and blood sugar control.
The Sunita Hydrocolloids Advantage in Pharmaceuticals
At Sunita Hydrocolloids, we recognize that the pharmaceutical industry demands the highest standards of purity, consistency, and regulatory compliance. Our commitment to quality ensures that our guar gum products are ideally suited for pharmaceutical applications:
- High Purity and Consistency: We provide pharmaceutical-grade guar gum that meets stringent quality control parameters, with minimal impurities and consistent performance in formulations.
- Tailored Viscosity Grades: Understanding that different applications require specific rheological properties, we offer various viscosity grades of guar gum to suit diverse formulation needs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Our manufacturing processes adhere to international quality standards, enabling our clients to meet global regulatory requirements for their drug products. These include Kosher, Halal, FSSC 22000, ISO 9001:2015, etc.
- Technical Expertise: Our team of experts possesses deep knowledge of guar gum chemistry and its pharmaceutical applications to provide valuable technical support and collaboration to our clients.
Conclusion
Guar gum’s ability to serve as a binder, disintegrant, suspending agent, and crucially, a modulator for controlled drug release, makes it a valuable asset in developing innovative and effective therapeutic solutions.
Guar gum’s multifunctionality as a pharmaceutical excipient is rooted in its unique natural properties. For a deeper understanding of its origin, structure, and broader applications, visit our comprehensive guide on what is guar gum.
For pharmaceutical companies seeking a reliable partner for high-grade guar gum, Sunita Hydrocolloids stands ready to meet your needs. Explore our products and connect with our experts to discuss how we can support your formulation challenges.
Explore Related Applications of Guar Gum
For a deeper understanding of guar gum’s versatility across industries and formulations, explore these related articles:
- Guar Gum in Oral Suspensions and Tablet Binding
Learn how guar gum enhances stability and performance in liquid and solid dosage forms, supporting effective drug delivery. - Why Natural Hydrocolloids Are Replacing Synthetic Additives in Food and Pharma
Discover the growing shift toward natural ingredients like guar gum in clean-label formulations across food and pharmaceutical sectors. - Guar Gum Applications in Cosmetics
Explore how guar gum contributes to texture, stability, and skin-friendly formulations in personal care and cosmetic products.





