Tara Gum vs Guar Gum: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Uses and Benefits
Food manufacturers across the USA are constantly weighing their additive options when it comes to achieving the right food texture, maintaining shelf stability and incorporating clean label ingredients. If you’re working with dairy, baked goods, sauces or beverages, you’ve probably asked: Which natural thickener can I use to get the best performance without compromising quality or compliance?
This is where hydrocolloids help. These plant based ingredients control viscosity, improve mouthfeel and extend shelf life. Two of the popular options are tara gum and guar gum. Both are galactomannans and natural thickeners, widely used across food categories with different properties and strengths.
Understanding the differences between these two – tara gum and guar gum is important. Whether you’re scaling up a formulation or switching suppliers, this guide breaks down their functions, use cases and performance so you can choose what works best for your product.
What Are Tara Gum and Guar Gum?
Knowing the origin and structure of tara gum and guar gum is essential to understanding what makes them behave differently in formulations. Both tara gum and guar gum are derived from plant seeds.
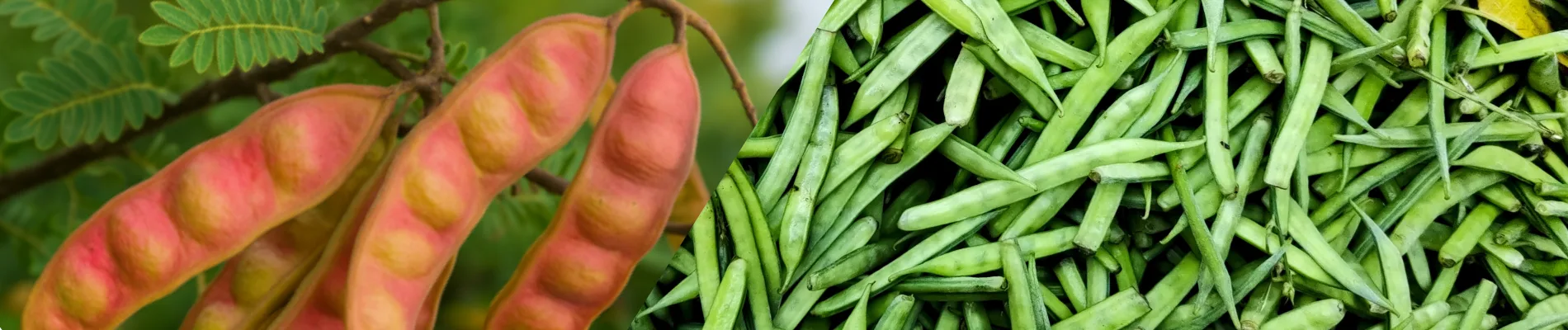
1. Tara Gum
It is sourced from the seeds of Caesalpinia spinosa, a leguminous shrub native to Peru. The seeds are processed into a fine powder through drying and milling, producing a gum that’s prized for its cold water solubility and freeze stability. It’s commonly used in frozen desserts, sauces and dairy applications.
2. Guar Gum
It comes from the seeds of Cyamopsis tetragonoloba, a drought resistant crop grown mainly in India and Pakistan. The seeds are dehusked, split and ground into powder. Guar gum is known for its high viscosity and fast hydration, making it ideal for beverages, baked goods and processed foods.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Both gums are galactomannans, meaning they’re made of mannose and galactose sugars. But their mannose to galactose ratios differ:
- Guar Gum has a ratio of 2:1 which gives it higher viscosity and faster hydration
- Tara Gum has a ratio closer to 3:1 offering better cold water solubility and smoother texture
This structural difference affects how each gum performs in food systems. Guar gum thickens quickly and strongly while tara gum provides a more refined texture and better flavor release.
Applications in the Food Industry
Whether you’re formulating frozen desserts, gluten free baked goods or ready to drink beverages, understanding how tara gum and guar gum perform in real food systems is crucial. Tara gum and guar gum are widely used in a variety of food products to improve texture and stability. These gums are often combined with other ingredients and other gums to achieve specific textures or functional properties in recipes.
Tara Gum Uses
- Ice cream and frozen yogurt: Inhibits the formation of ice crystals, improving texture, stability and mouthfeel
- Sauces and dressings: Maintains texture across pH ranges and temperature shifts
- Bakery fillings and glazes: Adds viscosity without affecting flavor
Guar Gum Uses
- Beverages: Stabilizes fruit particles and improves texture in juices and smoothies
- Soups and sauces: Adds body and prevents separation
- Gluten free baking: Acts as a binder to improve dough structure, elasticity and moisture retention
- Processed foods: Enhances shelf stability and texture in frozen meals and snacks
Comparison of Functional Properties
- Texture: Tara gum gives a smoother finish while guar gum can feel slimy if overused
- Hydration rate: Guar gum hydrates faster, ideal for instant mixes
- Gel formation: Tara gum forms soft gels with xanthan or carrageenan, influencing the form and consistency of gels in food applications while guar gum contributes to a different gel structure and final product form
- Flavor release: Tara gum allows better flavor perception especially in dairy and sauces
Both gums have their strengths. Choosing the right one depends on your product’s texture goals, processing conditions and label claims.
Health Benefits and Nutritional Value
Both guar gum and tara gum bring nutritional value and functional health benefits to the table making them more than just thickeners.
Guar Gum: Fiber Rich Functional Ingredient
Guar gum is a soluble dietary fiber that supports multiple health goals:
- Digestive health: Helps regulate bowel movements and promotes gut balance
- Cholesterol management: May reduce LDL levels by binding bile acids
- Blood sugar regulation: Slows glucose absorption, useful in diabetic friendly formulations
Tara Gum: Low Calorie Stabilizer
Tara gum also contains soluble fiber but its appeal lies in its low calorie profile and clean label credentials.
- Vegan and gluten free: Suitable for plant based and allergen sensitive diets
- Low allergen risk: Rarely linked to food sensitivities
- Texture without fat: Used in low fat desserts and frozen foods to mimic creaminess
It’s often chosen for products that need stability without added calories or allergens.
Safety and Regulatory Status
Both tara gum and guar gum are considered safe food substances and are approved as food additives by major regulatory agencies. They are approved for use by FDA, EFSA and Health Canada. Meeting international standards for food safety, they are widely accepted across global markets.
Performance Comparison: Tara Gum vs Guar Gum
Here, we compare tara gum and guar gum to discover which gum gives the best texture, stability and flavor control across different product formats.
| Feature | Tara Gum | Guar Gum |
| Source | Seeds of Caesalpinia spinosa (Peru, South America) | Seeds of Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (India, Pakistan) |
| Extraction Process | Drying and milling of seeds | Dehusking, splitting and grinding of seeds |
| Chemical Structure | Galactomannan with mannose to galactose ratio – 3:1 | Galactomannan with mannose to galactose ratio – 2:1 |
| Viscosity | Moderate viscosity, smoother texture | High viscosity at low concentrations |
| Hydration Rate | Slower hydration, cold water soluble | Fast hydration, ideal for instant mixes |
| Freeze-Thaw Stability | Excellent, suitable for frozen applications | Moderate, may degrade with repeated cycles |
| pH Stability | Stable across wide pH range | Stable in neutral to slightly acidic conditions |
| Flavor Release | Better flavor release, minimal masking | May mask flavors if overused |
| Common Uses | Ice cream, yogurt, sauces, bakery fillings | Beverages, soups, gluten free baking, processed foods |
| Health Benefits | Low calorie, soluble fiber, vegan, gluten free | High fiber, supports digestion, cholesterol and blood sugar control |
| Sustainability | Grown in high altitude regions with low water needs | Drought resistant crop, supports rural economies |
| Regulatory Approvals | Approved by EFSA, Canada | Approved by FDA, EFSA, Canada |
| Film Forming Properties | Forms edible films with moderate mechanical strength and flexibility; elongation at break (EB) is influenced by M/G ratio and heating | Forms edible films with high viscosity, good flexibility; elongation at break (EB) and film strength affected by M/G ratio and heating |
Thickening Power and Viscosity
Guar gum delivers higher viscosity at lower concentrations making it a cost effective thickener for large scale production. It hydrates quickly and builds body in beverages, soups and sauces without needing heat. This makes it ideal for instant mixes and cold processed foods. Its viscosity is consistent across batches which helps maintain product uniformity.
Freeze Thaw and pH Stability
Tara gum stands out in frozen and acidic applications. It resists ice crystal formation in frozen desserts and maintains texture through multiple freeze thaw cycles. Its stability across a wide pH range makes it suitable for acidic sauces, fruit fillings and dairy products. Tara gum also works well in formulations that undergo thermal processing or refrigeration.
Flavor and Texture Impact
Tara gum offers a smoother texture and better flavor release especially in dairy and sauces. It blends cleanly and doesn’t mask delicate flavors. Guar gum, while effective, can feel slimy or stringy if used in excess, which may affect mouthfeel in sensitive applications. The choice between tara gum and guar gum often depends on the specific recipe and the desired texture and flavor outcome. For brands focused on premium texture and taste, tara gum may be the better fit.
For suppliers offering food grade guar gum in the USA, this comparison helps customers match gum performance to their product goals. Whether the priority is cost, texture or processing stability, both gums have a place, just not always in the same formulation or recipe.
Sustainability and Sourcing
Sourcing food grade gums responsibly means working with suppliers who prioritize:
- Fair labor practices
- Transparent supply chains
- Sustainable farming methods
- Certifications that meet global standards
Choosing gums that are ethically sourced not only supports environmental goals but also strengthens brand trust with consumers who care about where their food comes from.
Which Is Better for Your Application?
Food brands in the USA often ask: Which gum fits my product best – tara or guar? The answer depends on your texture goals, processing conditions and nutritional claims. Here’s a quick breakdown to help you decide:
- Frozen desserts and acidic sauces: Go with tara gum for its freeze stability and smooth texture
- Beverages and gluten free baked goods: Choose guar gum for its high viscosity and fast hydration
- Low fat or vegan products: Tara gum works well as a stabilizer without adding calories
- Functional foods with fiber claims: Guar gum supports digestive health, cholesterol and blood sugar control
For US food brands, guar gum stands out for its versatility and nutritional edge. It’s a fiber rich ingredient that works across hot and cold applications from soups to smoothies. It also supports clean label goals and is widely accepted by regulatory bodies.
If you’re sourcing food grade guar gum in the USA, look for suppliers who offer consistent quality, transparent sourcing and technical support. Matching the right gum to your product is not just about texture—it’s about performance, compliance and consumer trust.
Conclusion
If your product needs clean label fiber claims, guar gum is a strong fit. If you’re working with frozen desserts or dairy, tara gum may perform better. Either way, choosing the right gum helps you hit texture goals and meet consumer expectations.
Looking for premium food grade guar gum in the USA? Contact us to source high quality, consistent guar gum backed by technical support and ethical sourcing. We help food brands get the performance they need without compromising quality.